Introduction to Read Model¶
Read model is an extra layer that separates templates and the application model. The read model is taken from CQRS pattern where the main idea is usage of different objects for reading and writing data.
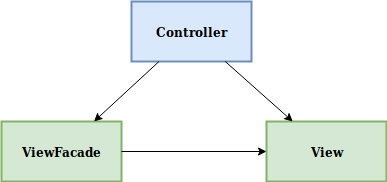
The read model stands next to the standard domain model, and it is completely independent of it. When using entities from the standard domain model, you might get a lot of data that you do not need for your particular use case. This is not effective and often has a negative impact on the application performance. Also, entities have a lot of responsibilities that are useless (or even harmful) during reading scenarios.
The main goal of the read model in Shopsys Framework is a clear separation of the model and view layer, and performance gain for the end user. This is achieved by avoiding the usage of Doctrine entities (and hence calls to SQL Database) in particular frontend templates.
Each object in the read model has its specific purpose (e.g. there is ListedProductView object that is used on product lists only).
Unlike the entities, objects in the read model contain solely the information that are necessary for a particular use case
and their data can be gathered from various sources (eg. Elasticsearch storage, and session).
Read model is a view on the model from a specific perspective - from the reading view. You are using the read model for reading use-cases only and therefore the read model can be simple and very optimized.
The objects in read model are immutable, read-only by definition, and do not have any behavior.
The read model is implemented in a separate shopsys/read-model package.
Read model options¶
Currently, you can choose between two implementations of ListedProductViewFacadeInterface that represents read model:
Option 1 - use data from Elasticsearch¶
- use
ListedProductViewElasticFacade(default) implementation ofListedProductViewFacadeInterfaceinservices.yamlandservices_test.yaml
Shopsys\FrameworkBundle\Model\Product\ProductOnCurrentDomainFacadeInterface: '@Shopsys\FrameworkBundle\Model\Product\ProductOnCurrentDomainElasticFacade'
Shopsys\ReadModelBundle\Product\Listed\ListedProductViewFacadeInterface: '@Shopsys\ReadModelBundle\Product\Listed\ListedProductViewElasticFacade'
- faster than getting products from SQL
- to use this implementation you need to use
ProductOnCurrentDomainElasticFacadeas well. You can find more about this topic in Front-end product filtering
Option 2 - use data from SQL database¶
- use
ListedProductViewFacadeimplementation ofListedProductViewFacadeInterfaceinservices.yamlandservices_test.yaml
Shopsys\FrameworkBundle\Model\Product\ProductOnCurrentDomainFacadeInterface: '@Shopsys\FrameworkBundle\Model\Product\ProductOnCurrentDomainFacade'
Shopsys\ReadModelBundle\Product\Listed\ListedProductViewFacadeInterface: '@Shopsys\ReadModelBundle\Product\Listed\ListedProductViewFacade'
- slower than Elasticsearch, but can be easily used for complex pricing models that calculate prices by SQL function
- to use this implementation you need to use
ProductOnCurrentDomainFacadeas well. You can find more about this topic in Front-end product filtering